Fracking has become a serious corporate threat to the environment and to all life within an extensive boundary of the drill site. One has to consider the hidden reasons for the idea of fracking, once you are fully aware of the dangers of radon the question then raised would be, why does the corporate realm believe a process of gas extraction is the way to go when they claim to have the authority and responsibility to act as guardians of the populations? I think they call it duty of care when it suits.
There are so many dangers from the actions of the almighty corporate banking state such as chemtrails, food additives, chlorine in the water which reacts with the fats in the food and deposits it in the arteries, fluoride in all the beers and anything else they can get the stuff into, vaccinations laced with metals and carcinogenic chemistry. Something is going on with the corporations that is not in the public interest or conducive to our health.
Radon the Facts
The US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) and the Surgeon General’s Office have estimated that as many as 20,000 lung cancer deaths are caused each year by radon. Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer.
According to the US Environmental Protection Agency, (EPA) 4 pCi/L, s the recommended action level for radon exposure. 4 pCi/l means you are exposed to approximately 35 times as much radiation as the Nuclear Regulatory Commission in the US would allow, if that family was standing next to the fence of a radioactive waste site. (25 mrem limit, 800 mrem exposure)
Safety standards for carcinogens are established based on a 1 in 100,000 risk of death. Most scientists agree that the risk of death for radon at 4 pCi/l is approximately 1 in 100. At the 4 pCi/l EPA action guideline level, radon carries approximately 1000 times the risk of death as any other carcinogen. The action level is not a safe level, as there are no “safe” levels of radon gas.
The alpha radiation emitted by radon is the same alpha radiation emitted by other alpha generating radiation sources such as plutonium.
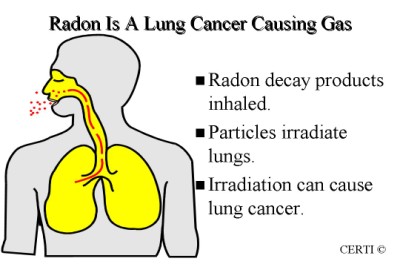
Radon is cancer-causing . You cannot see, smell or taste radon.
United States.
Scientific studies of radon exposure indicate that children may be more sensitive to radon.
Radon is a gaseous and highly radioactive element discovered by English physicist Ernest Rutherford in 1899. The discovery is also credited to German physicist Friedrich Ernst Dorn in 1900. More specifically, Rutherford discovered radon’s alpha radiation and Dorn discovered that radium was releasing a gas.
Radon is a colourless chemically-unreactive inert gas. The atomic radius is 1.34 angstroms and it is the heaviest known gas–radon is nine times denser than air. Because it is a single atom gas (unlike oxygen, O2, which is composed of two atoms) it easily penetrates many common materials like paper, leather, low density plastic (like plastic bags, etc.) most paints, and building materials like gypsum board (sheetrock), concrete block, mortar, sheathing paper (tarpaper), wood paneling, and most insulations.
Radon is also fairly soluble in water and organic solvents. Although reaction with other compounds is comparatively rare, it is not completely inert and forms stable molecules with highly electronegative materials. Radon is considered a noble gas that occurs in several isotopic forms. Only two are found in significant concentrations in the human environment: radon-222, and radon-220.
Radon-222 is a member of the radioactive decay chain of uranium-238.
Radon-220 is formed in the decay chain of thorium-232.
Radon-222 decays in a sequence of radionuclides called radon decay products, radon daughters, or radon progeny. It is radon-222 that most readily occurs in the environment. Atmospheric releases of radon-222 results in the formation of decay products that are radioisotopes of heavy metals (polonium, lead, bismuth) and rapidly attach to other airborne materials such as dust and other materials facilitating inhalation.
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas and comes from the natural breakdown (radioactive decay) of uranium. It is usually found in igneous rock and soil, but in some cases, well water may also be a source of radon.
The primary routes of human contamination to radon are inhalation and ingestion. Fracking is a method by which both water and air become contaminated with radon, in the chemical process of gas extraction, radon contaminates the groundwater, Although high concentrations of radon in groundwater may contribute to radon exposure through ingestion, the inhalation of radon released from water is usually more important, and the secondary means of ingestion via the burn off from the process called fracking.
More Data
Symbol: Rn
Atomic number: 86
Electron configuration: Xe 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p6
Boiling point: -61.85 °C
Melting point: -71.15 °C
Radon is obtained as a by-product of uraniferous ores processing after transferring into 1% solutions of hydrochloric or hydrobromic acids.
The gas mixture extracted from the solutions contains H2, O2, He, Rn, CO2, H2O and hydrocarbons.
The mixture is purified by passing it over copper at 720 °C to remove the H2 and the O2, and then KOH and P2O5 are used to remove the acids and moisture by sorption.
Radon is condensed by liquid nitrogen and purified from residue gases by sublimation.
The four principal ways of reducing the amount of radon accumulating in a house are :
Sub-slab depressurisation (soil suction) by increasing under-floor ventilation;
Improving the ventilation of the house and avoiding the transport of radon from the basement into living rooms;
Installing a radon sump system in the basement;
Installing a positive pressurisation or positive supply ventilation system.
Further Study
Over 100 new studies presenting the risks of fracking
Fracking